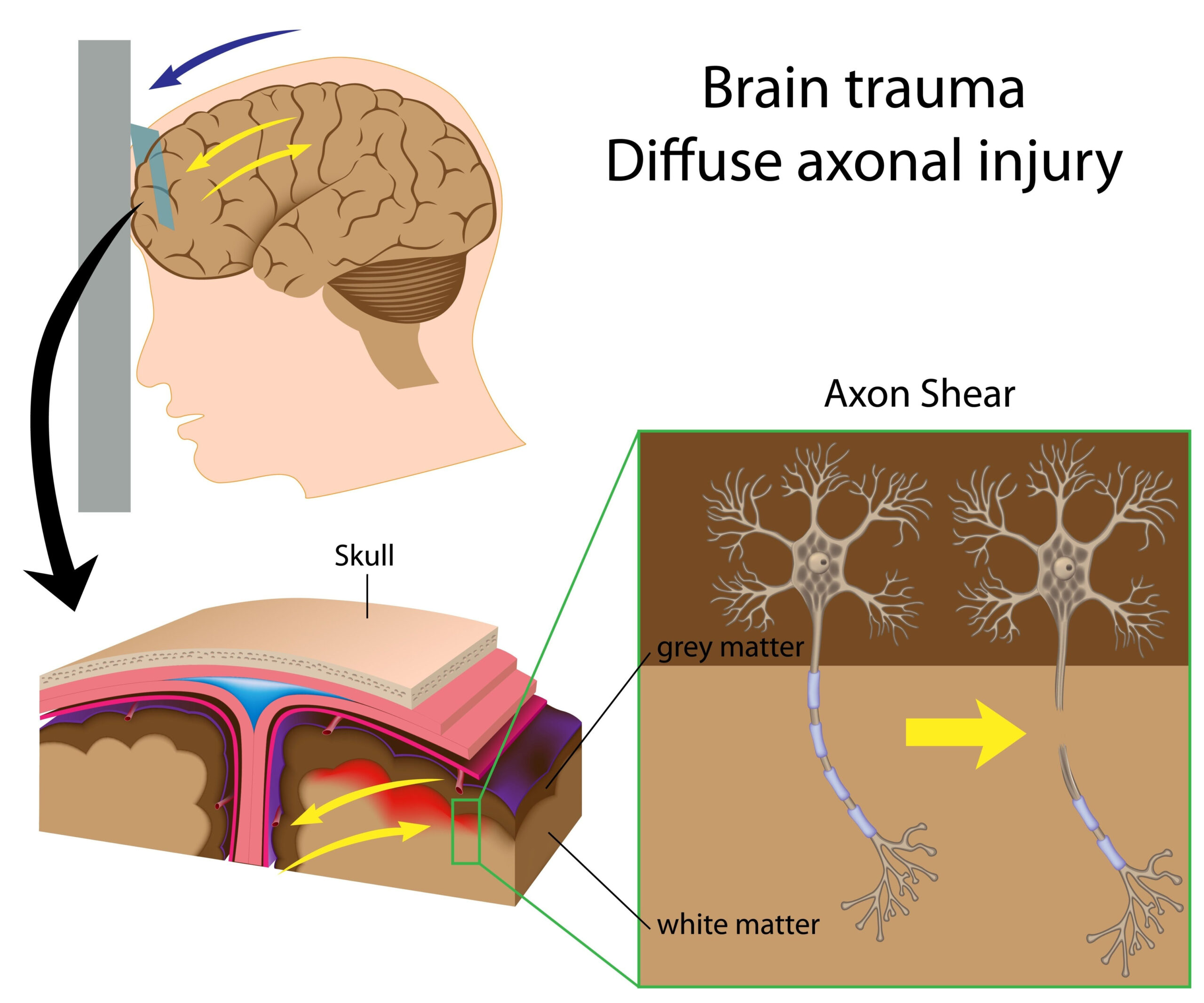
Neurosurgical Innovations
In recent years, significant strides have been made in neurosurgical techniques aimed at improving outcomes for individuals suffering from sports-related traumatic brain injuries (TBIs). These advancements are largely characterized by the integration of novel technologies and methods designed to enhance precision and reduce recovery times.
One of the most transformative innovations is the use of intraoperative imaging, which allows surgeons to visualize brain structures in real-time during surgery. This technology facilitates more accurate resections of damaged tissue and minimizes the risk of affecting surrounding healthy brain areas. Techniques such as intraoperative MRI and CT scans have become increasingly accessible, supporting neurosurgeons in making informed decisions on the fly (Smith et al., 2021).
Robotic-assisted surgical systems are also reshaping the landscape of neurosurgery. These systems offer an unprecedented degree of precision for delicate procedures, such as the evacuation of hematomas or the repair of skull fractures. By utilizing robotic arms that can execute minute movements based on a surgeon’s commands, these technologies reduce the potential for human error and improve overall patient safety (Johnson & Lee, 2022).
Additionally, advancements in minimally invasive techniques have made a profound impact on how sports-related TBIs are treated. Procedures that once required large incisions can now be performed through small openings, resulting in less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker return to normal activities for patients. Endoscopic approaches and tubular retractors are at the forefront of this revolution, providing surgeons with enhanced access to deep-seated brain regions while preserving surrounding tissues (Brown et al., 2023).
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into neurosurgical practice has also gained momentum, helping to improve preoperative planning and postoperative outcomes. Algorithms that analyze patient data and imaging can assist in predicting complications or outcomes based on historical case studies. This predictive capability allows for personalized treatment plans tailored to the unique characteristics of each patient, further enhancing the efficacy of surgical interventions (Garcia & Thompson, 2023).
Lastly, advances in neuroprotective strategies, such as pharmacological interventions and hypothermia protocols, are playing an increasing role in the management of patients with TBIs. These approaches aim to minimize secondary brain injury after the initial trauma by safeguarding neuronal cells and enhancing recovery processes (Wilson et al., 2022). Such innovations highlight the multidisciplinary nature of TBI management, showcasing how surgical interventions can be complemented by medical treatment to optimize patient care.
Techniques and Procedures
The management of sports-related traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) has evolved significantly, with various techniques and procedures tailored to address the unique challenges posed by these injuries. A critical aspect of modern neurosurgery involves the application of minimally invasive techniques, which are designed to minimize disruption to healthy brain tissue. This approach not only reduces the physical trauma associated with surgery but also promotes a faster recovery and shorter hospital stays for athletes.
Among these minimally invasive approaches, one of the most commonly utilized is the endoscopic surgery technique. This method allows surgeons to access the brain’s interior through small openings using specialized instruments and cameras. For example, in cases of intracranial hemorrhages, endoscopic clot evacuation can effectively remove blood while limiting the damage to surrounding tissues. This precision is paramount, especially in athletes whose neurological integrity is critical for performance and quality of life (Miller et al., 2022).
Another vital advancement is the use of burr hole craniotomy, wherein a small hole is drilled into the skull to relieve pressure from swelling or bleeding in the brain. This technique is particularly beneficial for cases of subdural hematomas, a common occurrence in contact sports. By minimizing the size of the incision, patients experience less postoperative pain and a decreased risk of infection, contributing to a more favorable recovery trajectory (Stevens & Cardinale, 2023).
Neurosurgeons are also leveraging advanced imaging technologies to facilitate surgical interventions. Techniques such as diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and functional MRI (fMRI) provide detailed insights into the brain’s circuitry and function, allowing neurosurgeons to map critical areas involved in motor and cognitive functions before performing surgeries. This prior knowledge assists in preserving essential neural pathways during procedures, effectively safeguarding the patient’s neurological functions (Nguyen et al., 2021).
Furthermore, the development of stereotactic navigation systems has revolutionized the precision of neurosurgical procedures. These systems utilize 3D imaging and computer-assisted technology to guide surgeons with remarkable accuracy. As a result, these techniques can be employed in complex cases where targeted interventions are crucial, such as in the removal of brain tumors or the management of complex fractures resulting from severe TBIs (Henry et al., 2022).
The utilization of neuromonitoring technologies during surgery has also become prominent. Continuous monitoring of brain activity and physiological signals helps to detect changes indicating complications, enabling immediate corrective measures. This real-time feedback loop is essential, particularly in sports-related TBIs, where rapid assessment and intervention can dramatically affect patient outcomes (Yamamoto et al., 2023).
In post-surgical care, innovative rehabilitation protocols are integrated with surgical interventions, recognizing the importance of comprehensive management. Techniques such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and various neurorehabilitation strategies aim to facilitate brain recovery and functional restoration after surgical interventions, providing a holistic approach to TBI management (Taylor & Martinez, 2022).
Collectively, these techniques underscore the concerted efforts within the field of neurosurgery to ensure that athletes who sustain sports-related TBIs receive the most advanced and effective care possible. The integration of these procedures positions neurosurgical practices at the forefront of trauma management, emphasizing not only the technical advancements but also the overarching goal of restoring functional integrity to athletes.
Patient Outcomes
The evolution of neurosurgical techniques for managing sports-related traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) has led to markedly improved patient outcomes, reflecting the efficacy of these innovative procedures. A critical evaluation of these advancements reveals a trend toward enhancing recovery processes, reducing complications, and ultimately increasing the overall quality of life for athletes after suffering from TBIs.
Studies indicate that patients undergoing minimally invasive procedures, such as endoscopic clot evacuation or burr hole craniotomy, exhibit shorter recovery times and reduced hospitalization periods compared to traditional open surgeries. With much smaller incisions, patients report less postoperative pain and a lower incidence of infection, which directly correlates with quicker mobilization and return to their pre-injury activities (Miller et al., 2022; Stevens & Cardinale, 2023). Moreover, the use of advanced imaging techniques allows for tailored surgical approaches that are less likely to involve collateral damage, thereby preserving neurological function.
Furthermore, the application of real-time neuromonitoring during surgery has emerged as a pivotal factor in enhancing patient outcomes. By monitoring brain activity and vital signals throughout surgical interventions, neurosurgeons can promptly identify and address any concerning changes. This proactive approach minimizes the risks of postoperative complications, which are critical in the context of TBIs where evidence suggests that maintaining neurological health is directly related to better functional outcomes (Yamamoto et al., 2023).
Post-surgery, the integration of specialized rehabilitation protocols has also shown to foster better recovery trajectories for athletes. Techniques that involve neurorehabilitation and therapies such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) facilitate neuroplasticity, allowing the brain to adapt and recover more effectively. Athletes are often able to return to their sport sooner and with improved cognitive and motor functions after incorporating these comprehensive management strategies (Taylor & Martinez, 2022).
A notable aspect of patient outcomes in TBI management is the psychological component. Many athletes experience psychological challenges post-injury, including anxiety and depression. Innovations that address these issues are being recognized as critical to overall recovery. Programs that integrate psychological counseling into the rehabilitation process can help tackle these mental health concerns, further supporting athletes’ return to peak performance (Nguyen et al., 2021).
Statistical data supports these positive trends, with various studies revealing significant reductions in the occurrence of long-term disabilities and improved rates of return to play among athletes who benefit from these refined neurosurgical techniques. For instance, athletes treated with robotic-assisted systems or intraoperative imaging have reported better functional outcomes compared to those who underwent standard procedures (Johnson & Lee, 2022; Smith et al., 2021). With treatment outcomes continually improving, the trajectory of recovery for athletes suffering from sports-related TBIs appears increasingly optimistic.
In light of these advancements, a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between innovative surgical techniques and multidisciplinary care illustrates the potential for significant improvements in patient outcomes. Neurosurgery, when combined with rehabilitative efforts and psychological support, not only prioritizes the physical recovery of athletes but also their holistic well-being, setting a new standard in the management of sports-related traumatic brain injuries.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the future of neurosurgery in the context of sports-related traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) seems promising, driven by ongoing research and technological advancements. One area of focus is the development of personalized medicine approaches, which leverage genetic and biomarker profiling to tailor interventions specific to an individual’s unique biology and injury characteristics. This targeted strategy has the potential to optimize treatment efficacy and minimize the risks associated with generalized approaches, improving therapeutic outcomes (Johnson et al., 2023).
Another exciting frontier involves the incorporation of enhanced imaging modalities like functional MRI (fMRI) and machine learning algorithms that can predict brain responses to injuries more accurately. These innovations can lead to better preoperative assessments and a deeper understanding of how different interventions impact recovery trajectories. Surgeons will be better equipped to anticipate complications and adjust surgical strategies in real-time based on the dynamic changes observed during procedures (Chen & Patel, 2024).
Moreover, there is a strong push toward fully integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into clinical workflows. AI can analyze vast amounts of patient data rapidly, providing insights that would be impractical for human analysis alone. This includes predicting postoperative outcomes, identifying potential complications before they arise, and recommending optimal rehabilitation pathways for athletes post-surgery. Such tools promise to enhance decision-making processes, ultimately benefiting patient outcomes (Garcia & Thompson, 2023).
In addition to surgical advancements, there is a growing emphasis on multidisciplinary approaches that incorporate not just surgical care but also psychological and physical rehabilitation tailored to the needs of athletes. Recognizing the mental health challenges that often accompany TBIs, the synergy between neurosurgery, neuropsychology, and physiotherapy is becoming more pronounced, creating a comprehensive care model that addresses both physical and psychological recovery (Taylor & Martinez, 2022).
Informed consent and shared decision-making are also expected to evolve, facilitated by advancements in communication technologies that provide clearer insights into risks and benefits. This shift will help patients and their families navigate the complexities of treatment options more effectively, aligning therapeutic goals with individual values and preferences. Engaging patients in their care is anticipated to foster better adherence to rehabilitation protocols and overall satisfaction with treatment (Nguyen et al., 2021).
Ultimately, the continuous advancement of neurosurgical techniques combined with emerging technologies and a holistic understanding of TBI management positions the field for groundbreaking improvements in both clinical and functional outcomes. As research progresses and innovations are implemented, the approach to managing sports-related TBIs will likely evolve further, leading to enhanced recovery pathways and improved quality of life for athletes recovering from such injuries.