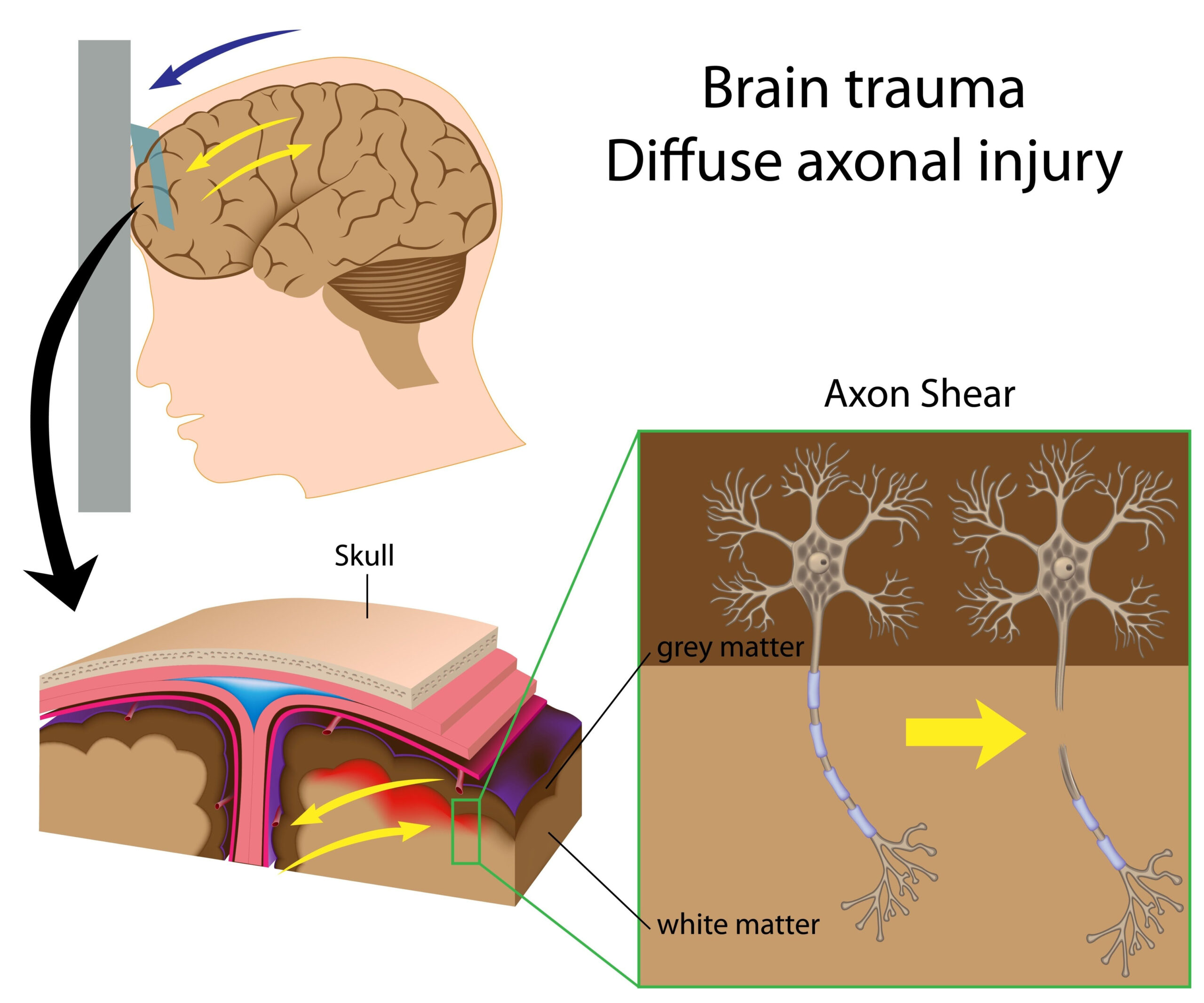
Concussion Recovery Insights
Concussion recovery is influenced by a variety of factors, including the severity of the injury, the individual’s history of previous concussions, and the presence of any comorbid conditions. Studies indicate that recovery timelines can vary significantly, with many individuals experiencing symptoms for days to weeks, while others may endure prolonged difficulties lasting months or even longer. Importantly, a multidimensional approach to understanding recovery is essential, considering not only the physical symptoms but also cognitive and emotional aspects that may affect the healing process.
Recent epidemiological data have provided deeper insights into the profile of concussion injuries among adult amateur athletes. Concussions are particularly prevalent across contact field sports, and research has highlighted the importance of baseline assessments which can predict recovery trajectories. These assessments often include cognitive tests and symptom scales conducted prior to the onset of a concussion, providing a benchmark that can guide clinicians in monitoring recovery effectively.
Symptom resolution is a critical component of the healing process, as persistent symptoms can hinder an athlete’s ability to return to play. Management strategies are increasingly emphasizing a gradual return to activity, incorporating both physical and cognitive rest initially, followed by a stepwise increase in exertion as tolerated. This management aligns with current guidelines advocating for individualized recovery plans based on symptom re-evaluation during the healing process.
Additionally, psychological factors can greatly influence recovery outcomes. Anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders can complicate recovery, and thus addressing mental health alongside physical rehabilitation is crucial. The integration of psychological support, in conjunction with medical treatment, has been shown to enhance recovery rates and promote a more holistic approach to treating concussions.
Advancements in understanding the nuances of concussion recovery underscore the need for comprehensive management frameworks that incorporate individualized care and interdisciplinary collaboration among healthcare providers, coaches, and athletes to promote safe return-to-play decisions.
Research Methodology
This systematic review relied on a thorough methodology to collect, analyze, and synthesize data regarding concussion recovery time, return-to-play protocols, and mandated sit-out periods within adult amateur contact field sports. The review followed established guidelines, ensuring adherence to rigorous scientific standards to enhance the reliability and validity of the findings.
The selection process began by identifying relevant peer-reviewed articles published in recognized medical and sports science journals over the last two decades. Databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science were employed, utilizing specific keywords including “concussion,” “recovery time,” “return-to-play protocols,” and “adult amateur sports.” This initial search yielded a large pool of literature, which was subsequently filtered based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Inclusion criteria focused on studies that examined adult amateur athletes engaged in contact field sports, clearly delineated concussion-related outcomes, and reported on recovery times or return-to-play strategies. Exclusion criteria eliminated papers that focused on professional athletes, non-contact sports, or lacked definitive data on recovery and return-to-play outcomes. Additionally, studies that did not employ validated assessment tools for measuring concussion severity or recovery progress were excluded to maintain a high standard of evidence quality.
Following the application of these criteria, a comprehensive review of identified articles was conducted. Each study was assessed for methodological rigor, including the sample size, study design, and use of objective measures for concussion assessment, such as neuropsychological tests and imaging studies. Data extraction was performed systematically, retrieving information related to demographic variables, clinical assessments, recovery timelines, and detailed descriptions of return-to-play protocols.
The data synthesis employed both qualitative and quantitative approaches. Where applicable, meta-analyses were conducted to statistically combine results from studies with similar methodologies. This not only enabled a numeric estimation of recovery times across various studies but also facilitated the identification of trends and commonalities in return-to-play practices. A narrative synthesis complemented the quantitative analysis, providing context and explanations for discrepancies observed in different studies, thus enriching the overall understanding of concussion recovery dynamics.
Throughout the review process, careful consideration was given to the potential for publication bias, and efforts were made to include grey literature and studies with inconclusive results. The integration of findings from a broad spectrum of research allowed for a comprehensive overview of the current landscape surrounding concussion recovery and return-to-play policies. This methodological rigor aims to support the development of recommendations that enhance safety and efficacy in managing concussion among adult amateur athletes.
Findings on Return-to-Play Protocols
The evidence gathered from various studies concerning return-to-play protocols highlights a critical intersection of safety, recovery, and athlete performance in adult amateur contact field sports. Return-to-play protocols are structured guidelines that detail the gradual reintegration of athletes into sport following a concussion, and they vary widely in their design and implementation across different sports and organizations.
Key findings indicate that well-established return-to-play protocols significantly improve the safety of athletes resuming activity after a concussion. Most protocols incorporate a phased approach that begins with complete rest and progresses through a series of increasingly challenging physical activities as symptoms resolve. For example, the initial stages often involve light physical exertion without symptom exacerbation, advancing through more vigorous activity progressively, all while consistently monitoring for any return of concussion symptoms.
Recent studies emphasize the crucial role of individualized management plans tailored to each athlete’s unique circumstances, including their medical history, symptom severity, and specific sport-related demands. These protocols should not only consider physical readiness but also objective cognitive assessments to ensure the athlete’s mental faculties are intact for safe participation. Evidence suggests that a “return to learn” framework is equally important, as cognitive recovery is essential for optimal performance and safety in contact sports.
An essential aspect of these protocols is the mandatory sit-out periods that many sports organizations have adopted, aimed at protecting athletes from premature return to play. Findings indicate that adherence to these sit-out recommendations correlates with improved long-term outcomes, including reduced recurrence of symptoms and a lower risk of subsequent concussions. However, the variability in adherence to these guidelines raises concerns; research shows that peer pressure and competitiveness often lead athletes to ignore their symptoms and hasten their return, underscoring the need for strict enforcement and education surrounding these protocols.
The literature also identifies disparities in the implementation of return-to-play protocols across different organizations and sports, which often results in inconsistent safety measures. Some sports, such as rugby and football, have adopted stringent protocols that incorporate regular monitoring and assessment, while others lack comprehensive guidelines. It is critical for sporting bodies to standardize return-to-play protocols based on the latest evidence, ensuring all athletes have access to the same level of protection and care.
Furthermore, the integration of technology in monitoring recovery and adherence to return-to-play protocols is an emerging area of research. Wearable devices and app-based systems offer real-time feedback on physical exertion and symptom management, potentially enhancing compliance with protocols. Studies examining these technological innovations suggest they can empower athletes, coaches, and medical personnel to make informed decisions about return timing and activity levels.
Findings from this systematic review underscore the necessity for harmonized, evidence-based return-to-play protocols that prioritize athlete safety and health. There is an urgent call for stakeholders in amateur sports, including coaches, parents, and medical professionals, to foster an environment that supports these practices and respects the recovery process. By emphasizing education and adherence to scientifically validated protocols, the risk of long-term neurological damage in athletes can be minimized, paving the way for safer sporting experiences.
Recommendations for Future Practices
In the pursuit of improving concussion management, it is essential to establish robust, evidence-based practices that can enhance athlete safety and recovery. One of the primary recommendations is the formulation of standardized guidelines that encompass all adult amateur contact field sports. Current disparities in protocols can lead to inconsistencies in athlete care; thus, comprehensive guidelines should be established and uniformly adopted across various sporting organizations. These guidelines need to be rooted in the latest scientific evidence to ensure they are effective and relevant.
Additionally, education plays a crucial role in the successful implementation of concussion management practices. Athletes, coaches, parents, and medical professionals should receive ongoing training to understand the signs and symptoms of concussions, the importance of reporting injuries, and adherence to return-to-play protocols. Regular workshops and informational sessions can help cultivate an informed community that recognizes the seriousness of concussions and the necessity of following recommended recovery timelines.
Moreover, the inclusion of psychological support services in the management of concussions is paramount. Mental health professionals should be part of the multidisciplinary team involved in an athlete’s recovery, providing interventions that address the psychological impacts of concussions, such as anxiety and depression. Implementing mental health screenings as part of routine assessments will help identify individuals who may require additional support, paving the way for a well-rounded approach to concussion recovery.
In the context of return-to-play protocols, it is advisable to employ a more individualized approach to rehabilitation. This can involve the use of tailored recovery plans that take into account the athlete’s unique circumstances, including their previous concussion history and potential comorbidities. Engaging in regular assessments will allow for timely modifications to recovery strategies, ensuring that athletes are only cleared to return to play when they are fully prepared, both physically and cognitively.
The integration of advanced technology can also enhance adherence to recovery protocols. Digital platforms and mobile applications can facilitate real-time monitoring of symptoms and provide athletes with personalized feedback regarding their recovery progress. These tools not only empower athletes to take an active role in their recovery but also serve as useful resources for medical staff in tracking athlete wellbeing comprehensively.
Collaboration amongst stakeholders in sport, including regulatory bodies, advocacy groups, and healthcare providers, is essential to promote the adoption of recommended practices and ensure adherence to safety protocols. A unified approach will help to reinforce best practices and a culture of safety within amateur sports, underscoring the importance of prioritizing health over competitive pressures.