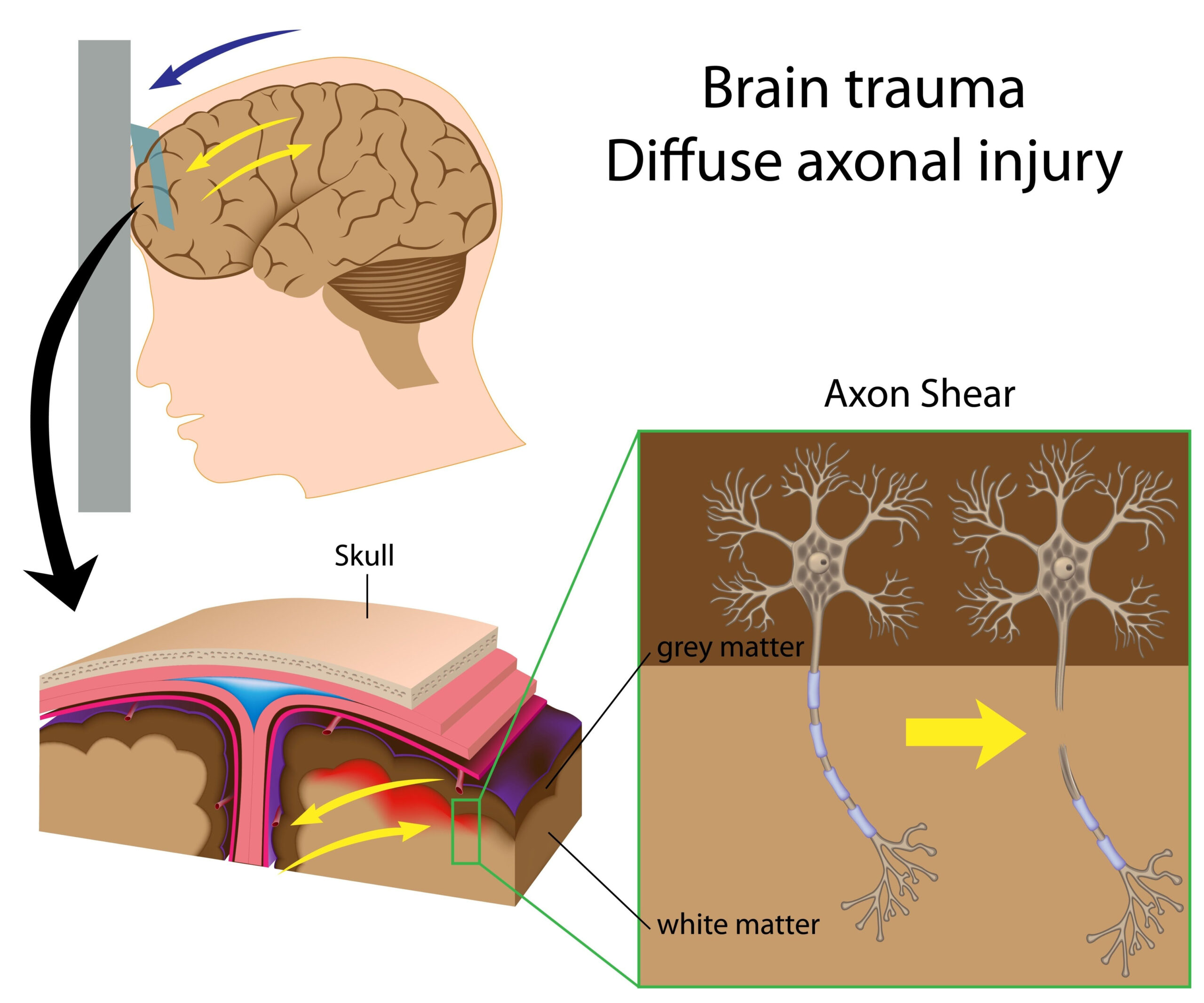
Overview of Concussion Care
Concussion care encompasses a multifaceted approach aimed at addressing the complexities of mild traumatic brain injuries. These injuries often occur in sports and recreational activities, leading to potential long-term consequences if not managed correctly. A critical aspect of concussion care involves immediate recognition and appropriate response following an injury. This requires not only symptom awareness but also an understanding of the neurophysiological aftermath that a concussion can provoke.
Initially, the approach to concussion management revolves around the assessment of symptoms and the determination of their severity. Common symptoms include headaches, dizziness, confusion, and balance issues. Healthcare providers utilize standardized tools, such as the Glasgow Coma Scale, alongside symptom checklists, to evaluate the patient’s condition. A comprehensive evaluation is crucial, as even mild symptoms can signify significant underlying brain injury.
Following the assessment, a structured plan for recovery is essential. Rest is the primary recommendation, as the brain requires time to heal. However, rest should be balanced with gradual return to normal activities to avoid prolonged recovery times. This approach often includes a stepwise process where patients progressively return to cognitive and physical exertion under medical guidance.
Moreover, educational initiatives play a pivotal role in enhancing understanding of concussions among athletes, coaches, and parents. Effective education can lead to better recognition of concussion symptoms and promote appropriate responses to injuries when they occur. This emphasis on education aids in creating a culture of safety that prioritizes the health and well-being of those at risk for concussions.
Collaboration among healthcare providers, educators, and sports organizations is also vital in shaping efficient concussion management protocols. By establishing clear communication channels and shared resources, stakeholders can implement evidence-based practices that reflect the latest research findings. Additionally, continuous training and updates for medical staff and coaches can foster an environment where concussion care is not only reactive but also proactive.
Finally, ongoing research continues to shed light on the long-term impacts of concussions, informing best practices in care and education. As understanding deepens regarding the neurobiological effects of concussions, the protocols surrounding concussion management evolve, ensuring that care practices align with the most current evidence. This ongoing commitment to research and education is essential in safeguarding the health of individuals susceptible to concussions, ultimately leading to better outcomes and quality of life.
Research Methodology
To thoroughly investigate the landscape of compassionate concussion care, a scoping review methodology was utilized. This approach allows for an expansive exploration of the field, capturing a wide range of literature and insights while retaining the flexibility necessary to navigate varying definitions, contexts, and applications of concussion management.
The initial phase of the research involved establishing clear inclusion criteria for relevant studies. This included peer-reviewed articles, clinical guidelines, and educational materials published within the last fifteen years, hence ensuring that the findings reflect contemporary practices and knowledge in concussion care. The focus was on those documents addressing educational perspectives on concussion management, highlighting how compassion plays a role in care delivery.
An extensive literature search was conducted across multiple databases including PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar. Keywords such as “concussion care,” “compassionate care,” “mild traumatic brain injury,” and “educational initiatives” guided this inquiry, ensuring a robust collection of resources. Initially, thousands of articles were screened for relevance; subsequent analysis yielded a more manageable selection that met the rigorous criteria set forth.
The selected studies were then evaluated for their methodological quality. This entailed examining the design of each study—whether qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods—and assessing the appropriateness of the respective methodologies for addressing the research questions posed. This evaluative component enabled the identification of gaps and opportunities for further research in the realm of compassionate concussion care.
Data extraction focused on several key themes, including the educational interventions employed, the effectiveness of these initiatives in raising awareness about concussion signs and symptoms, and how these programs foster a supportive environment for individuals recovering from brain injuries. Special attention was given to how compassion in care was defined and operationalized within the studies, as this offered insights into the practical application of compassionate care principles.
Furthermore, thematic analysis was employed to synthesize findings across the reviewed literature. This facilitated a deeper understanding of the relationships between educational efforts, provider attitudes, and the overall quality of care delivered to concussed individuals. It also highlighted how educational programs could better incorporate principles of empathy and understanding, pivotal for enhancing patient experiences and outcomes.
Through this comprehensive scoping review, pivotal insights have emerged, laying the groundwork for future exploration and refinements in concussion care education. By aggregating a spectrum of perspectives and findings, this research methodology not only enriches the current knowledge base but also emphasizes the importance of implementing compassionate care practices within concussion management frameworks.
Results and Insights
The findings from this scoping review underscore several critical insights surrounding the implementation of educational initiatives in compassionate concussion care. A significant theme that emerged was the efficacy of targeted educational programs in enhancing awareness of concussion symptoms among various stakeholders, including athletes, coaches, parents, and healthcare providers. These programs frequently employed interactive methods—such as workshops, simulations, and webinars—to engage participants and facilitate comprehensive understanding. The reviews indicated that when education is delivered in an accessible and relatable format, retention of information improves significantly, leading to more prompt recognition of concussion symptoms and, consequently, better outcomes for those affected.
Another notable insight involved the role of compassion in concussion management. Studies highlighted that healthcare providers who displayed empathy and understanding towards patients experienced an increase in patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment protocols. Compassionate communication was shown to foster trust, encouraging patients to share their symptoms honestly, which is crucial for accurate assessment and recovery planning. Moreover, compassionate care was frequently linked to reduced anxiety levels in patients, leading to a more favorable recovery trajectory. This finding aligns with literature emphasizing the holistic nature of healthcare, wherein emotional and psychological support interplays with physical recovery.
The results also illustrated disparities in education and understanding of concussion care across different levels of sport. For instance, youth sports organizations often lacked the resources compared to professional teams, highlighting a need for equitable access to educational materials and training for all athletes regardless of their competitive level. Furthermore, there was a correlation identified between comprehensive educational interventions and improved implementation of concussion protocols within sports organizations. Educational efforts that included stakeholders at all levels resulted in the establishment of supportive environments conducive to effective concussion care, thus emphasizing the importance of a community-based approach.
Several studies identified key barriers to effective concussion management, including insufficient training for coaches and volunteers who are often the first responders in sports settings. The lack of formal education in recognizing and responding to concussions led to delayed treatment and sometimes severe repercussions for the athletes involved. Increasing the knowledge base of these individuals was repeatedly portrayed as a crucial step in mitigating the risks associated with concussions.
Additionally, the data revealed variations in the implementation of concussion protocols across institutions, influenced in part by local legislation and organizational policies. In regions with stringent laws enforcing concussion management, adherence to best practices demonstrated a marked improvement, suggesting that policy frameworks can significantly impact care outcomes. These insights call for advocacy and the development of standardized guidelines that not only facilitate educational outreach but also ensure compliance with best practices across the board.
Significantly, the analysis underscored the importance of continuous professional development in the field of concussion care. As research into mild traumatic brain injuries progresses, regular updates and refreshers for healthcare providers and educational leaders became evident as essential components for effective long-term management of concussions. Ongoing education ensures that practices remain current and that all stakeholders are prepared to respond appropriately, reinforcing a culture of safety and support.
In summary, the results of the scoping review paint a robust picture emphasizing the integration of educational initiatives centered around compassion in effective concussion care. These findings advocate for the creation of comprehensive, empathetic, and proactive approaches that not only treat concussions but also empower individuals and communities to recognize and respond to these injuries with urgency and understanding.
Future Directions in Education
As the landscape of concussion management continues to evolve, it’s imperative to explore future directions for educational initiatives that enhance compassionate concussion care. The integration of evidence-based practices with innovative educational strategies presents a unique opportunity to elevate the standard of care for individuals affected by concussions.
One promising direction involves the incorporation of technology into educational programs. Advances in digital platforms enable the development of interactive e-learning modules that cater to diverse learning styles. Virtual simulations and mobile applications can serve not only to educate athletes and coaches but also to provide accessible resources for parents and healthcare providers. By harnessing technology, it’s possible to create engaging educational experiences that improve retention of information and promote proactive participation in concussion management.
Furthermore, partnerships between educational institutions, healthcare systems, and sports organizations can facilitate the development of standardized curricula dedicated to concussion awareness and management. Integrating concussion education into existing health education frameworks at schools and universities would empower students with knowledge from an early age. This foundational understanding, coupled with hands-on training, could cultivate a generation that prioritizes health and safety in sports.
Collaboration extends to community-based initiatives, where workshops and information sessions can be tailored to specific populations, particularly underserved communities who may have limited access to resources. Reach-out programs that focus on educating local coaches, recreational sports leagues, and youth organizations can create a ripple effect, as informed leaders foster safer environments for their athletes. Tailoring content to resonate with different demographics ensures inclusivity and maximizes the impact of these educational efforts.
Moreover, it is essential to involve convalescing athletes in educational initiatives. Peers often wield significant influence, and programs that incorporate testimonials from athletes who have experienced concussions firsthand can resonate more deeply than traditional didactic methods. By sharing their stories and recovery journeys, these individuals can inspire openness about concussion symptoms, encourage other athletes to seek help promptly, and combat the stigma that may come with reporting an injury.
Continued professional development for healthcare providers is critical to ensure alignment with the latest concussion care guidelines. Regular training sessions that emphasize the significance of compassionate communication and patient-centered care can equip providers to better support their patients emotionally and psychologically. Educators in medical and allied health fields should incorporate discussions on empathy and compassion within their training programs, reinforcing the importance of treating patients as individuals rather than mere cases.
Data collection and research should also remain a priority in shaping future educational strategies. Ongoing studies examining the efficacy of various educational approaches will be instrumental in determining best practices. Quantitative and qualitative research can shed light on which methods achieve the best outcomes in terms of awareness, recognition of symptoms, and adherence to concussion protocols. Continuous feedback loops from both educators and participants will help refine programs, ensuring they remain relevant and effective.
Finally, advocacy for supportive policies at local, state, and national levels is critical. Policymakers must be engaged in discussions about the necessity of comprehensive education on concussion management for all stakeholders, particularly in youth sports. Legislation mandating educational standards in concussion care can lead to the uniform implementation of best practices, enhancing safety measures across all levels of sport.
By focusing on these future directions, educational initiatives can play a pivotal role in transforming the approach to concussion care. Emphasizing compassion and empathy within educational frameworks not only cultivates a deeper understanding of concussions but also fosters a culture of care that prioritizes health, safety, and well-being for all individuals involved in sports and physical activities.